Global warming

This refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. These shifts may be natural, but in the past 200 years, human activities have largely influenced climate change, primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels (like coal, oil and gas), which produces greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases
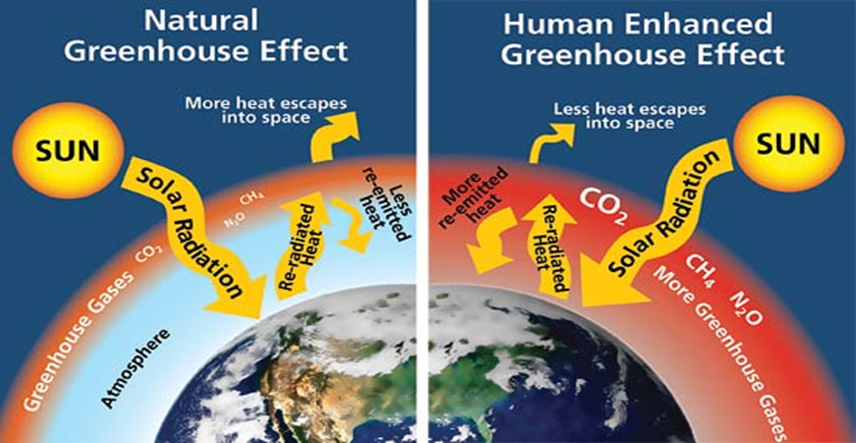
These gases cause global warming by trapping the sun’s heat and stopping it from leaking back into space. Green house gases contribute to respiratory diseases arising from smog and air pollution. The main greenhouse gases whose concentrations are rising are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and ozone in the lower atmosphere. CO2 produced by human activities is the largest contributor to global warming.
Human activities producing greenhouse gases

The generation of electricity. Electricity is often generated by burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, or gas, which produces carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide.
Deforestation. Yearly, approximately 12 million hectares of forest are cut down. Trees act as filters by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. Their destruction limits nature’s ability to keep greenhouse gases out of the atmosphere Use of vehicles. Vehicles such as cars, ships and airplanes run on fossil fuels making them a major contributor of carbon dioxide emissions. Transport accounts for nearly one quarter of global energy-related carbon-dioxide emissions with road vehicles accounting for the largest emissions, due to the combustion of petroleum-based products, like gasoline, in internal combustion engines.
Effects of global warming

Warmer temperatures lead to an increase in the frequency, intensity, and duration of heat waves. This poses health risks such as heat strokes, particularly for young children and the elderly. Homeless people are also affected by these extreme climate changes.Climate change can also impact human health by worsening basic amenities needed for survival like air and water quality. This increases the spread of aerobic and waterborne diseases.
Rising sea level threatens coastal communities and ecosystems.
Changes in the patterns and amount of rainfall, as well as changes in the timing and amount of stream flow, can affect water supplies and water quality and the production of hydroelectricity. This also impacts food production as crops will fail to grow.Changing ecosystems influence geographic ranges of many plant and animal species and the timing of their lifecycle events, such as migration and reproduction.
How to combat global warming
New alternatives such as solar systems should be adapted by more households and industries to lessen the carbon emission of electricity producing companies that use fossil fuels.
Deforestation should be abolished by adapting new governmental policies. In its place, policies that encourage afforestation and re-forestation should be implemented.
The use of renewable energy sources should be introduced to power vehicles as opposed to fossil fuels. In the event that the larger populations are unable to purchase such vehicles, public transport systems can be introduced and encouraged as opposed to private means to lessen carbon emissions in areas with large vehicle traffic.
article by: zelma sera
